Role of Power Wirewound Resistors in Industrial Control
Role of Power Wirewound Resistors in Industrial Control
In the modern industrial landscape, electrical components play an essential role in the functionality and reliability of machinery and equipment. One such critical component is the power wirewound resistor, renowned for its high precision and robust performance.
Understanding Power Wirewound Resistors
Definition and Construction
Power wirewound resistors are passive electrical components that manage current flow within electronic circuits. They are made by winding a metal wire—typically nichrome or manganin—around an insulating core, usually ceramic or fiberglass. This configuration allows them to handle substantial power levels while dissipating heat effectively.
The resistive wire is complemented by protective coatings, such as vitreous enamel, that enhance durability and thermal stability, making them operable under high-temperature conditions.
Key Materials Used
The functionality of power wirewound resistors is significantly influenced by the materials used in their construction:
Resistive Wire: Commonly made from high-resistance alloys like nichrome, offering excellent heat resistance and stability.
Core Materials: Ceramic or fiberglass is preferred for their insulating properties and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Coating Materials: Vitreous enamel is often employed to protect the resistor from environmental factors.
Working Principle
The functioning of these resistors is based on Ohm's Law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance. The wound wire effectively converts electric energy into heat through its resistance, allowing it to limit current flow within a circuit without failure. Wirewound resistors maintain stable performance even under fluctuating temperatures, making them a reliable choice in industrial applications.
Types of Power Wirewound Resistors
General Purpose Wirewound Resistors
These versatile resistors cater to a broad spectrum of applications, providing a stable performance at a relatively low cost.
Precision Wirewound Resistors
Designed for applications requiring high accuracy, these resistors operate with tight tolerances significantly improving measurement reliability.
Safety Wirewound Resistors
These incorporate flame retardant coatings that prevent overheating, ensuring safe operation and extending operational life.
Fusible Wirewound Resistors
Fusible designs offer self-protecting features; they burn out under excess load without production of flames, providing a safer alternative for circuit protection.
Pulse Wirewound Resistors
Specially designed to handle short-duration impulse events, these resistors can withstand power surges, making them ideal for applications where momentary high energy is commonplace.
Applications in Industrial Control
Role in Power Electronics
Power wirewound resistors are prevalent in power electronics, specifically in voltage regulation and power conversion. They dissipate heat generated by high currents, ensuring the reliability of power supplies and motor drives.
In Motor Controls
These resistors are fundamental in motor control applications, where they help manage the start and stop phases while facilitating effective energy management.
Temperature Sensing Applications
Wirewound resistors also find a niche in temperature sensing systems. Their stability and low temperature coefficients make them ideal for accurate thermometric measurements and control processes.
Advantages of Power Wirewound Resistors
High Power Handling Capability
Their robust design allows wirewound resistors to handle high power levels, crucial for industrial equipment that operates under strenuous conditions.
Precision and Stability
Wirewound resistors provide high precision with low temperature coefficients, ensuring that resistance values remain stable across a range of operating conditions—a must-have for applications requiring accuracy.
Low Temperature Coefficients
Their low temperature coefficients signify minimal resistance drift, enabling consistent performance in circuits subjected to varying temperature conditions.
Considerations for Selecting Power Wirewound Resistors
Resistance Values and Tolerance Levels
It is essential to select a resistor whose resistance value aligns with the application requirements to prevent circuit inefficiencies.
Power Ratings and Heat Management
Evaluating power ratings is critical since exceeding these limits can lead to overheating. Proper heat management—often through heatsinks or appropriate mounting—is essential.
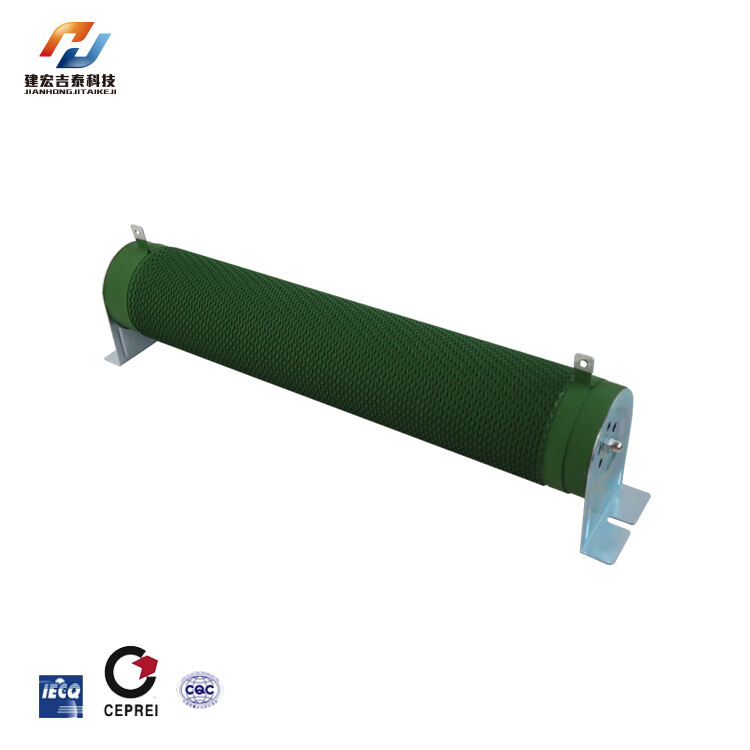
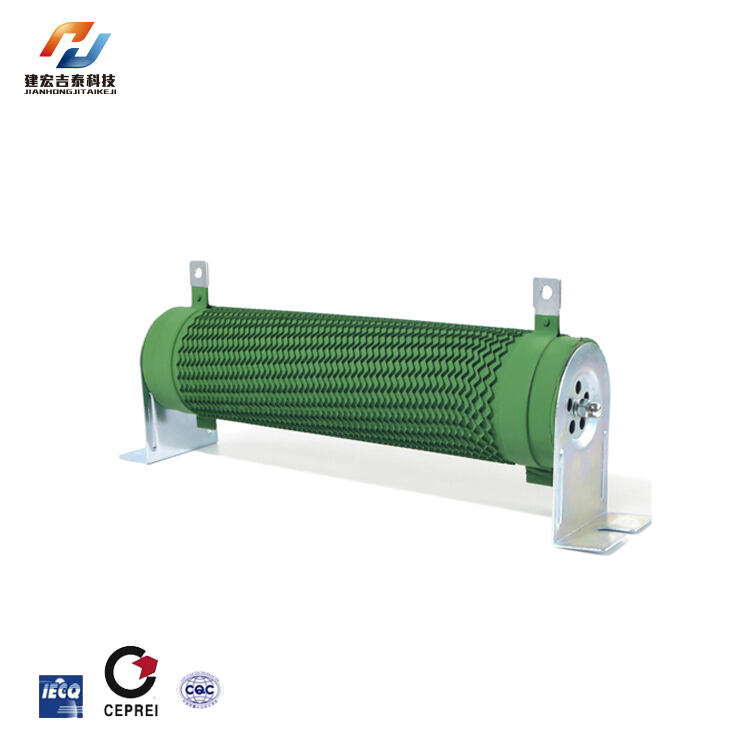
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
What Are The Functions Of The Ac Load Box For Power Supply Detection And Maintenance
2024-01-11
-
The Use Characteristics And Methods Of The Load Bank Of The Generator Set
2024-01-11
-
The function of the load bank
2024-01-09
-
Explore The Types And Characteristics Of Resistors: Fixed And Variable Resistors
2024-01-09
-
How Resistors Work And Their Applications In Circuits
2024-01-09
-
Load Banks: Ensuring Optimal Performance in Power Testing Environments
2024-10-21
-
Exploring the Advantages of Wirewound Resistors for Precision Applications
2024-10-14
-
Understanding the Benefits of Aluminum Resistors in High-Performance Applications
2024-10-08

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 BN
BN
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 NE
NE
 MY
MY
 UZ
UZ













